Manipulator model performance refers to how well a model makes reliable predictions compared to the physical manipulator model and the validity of those predictions.
Control performance, on the other hand, relates to how effectively a system or process is managed or regulated to achieve desired outcomes. In the context of model control, it could refer to the ability to maintain stability, optimise parameters, and ensure consistent results under varying conditions. Monitoring control performance helps identify issues and make adjustments to improve overall system efficiency and accuracy.
In this section, we present the model and control performance of three different control models: simplified PID, conventional PID, and time-delayed Extended Kalman Filter-based trajectory tracking control.
You can find more details of the control performance here.
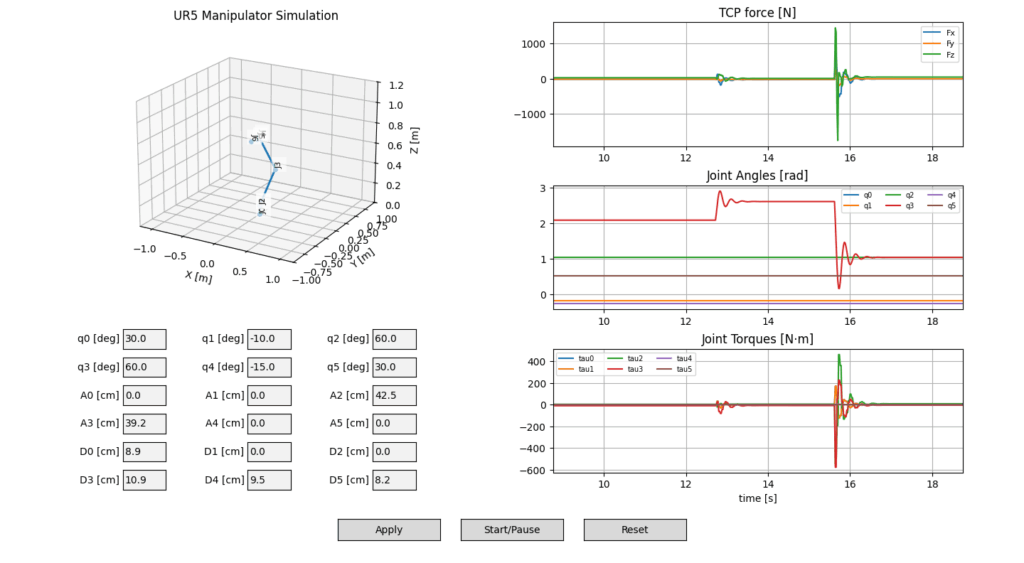
Figure 1. Force and Torque Damping characteristics with the Simplified PID control.
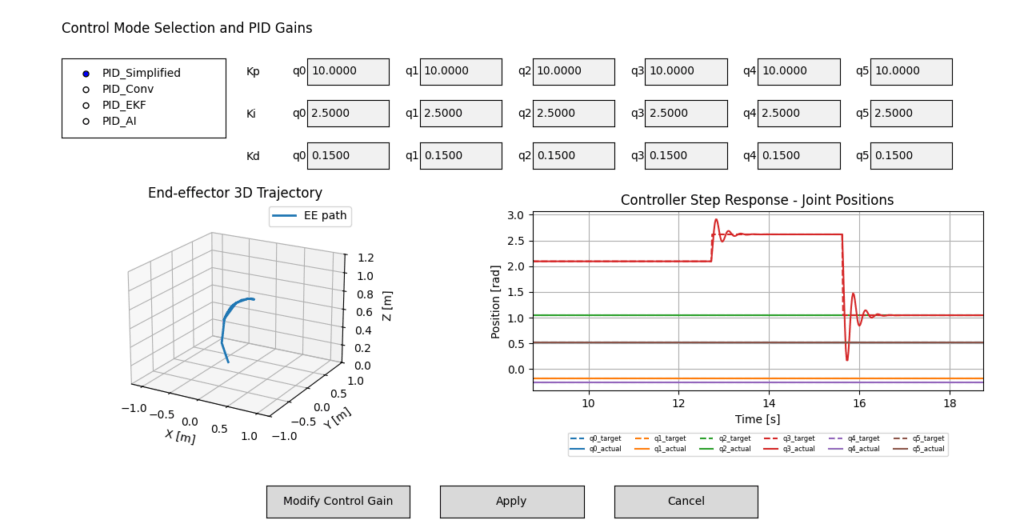
Figure 2. Control response of the Simplified PID control.
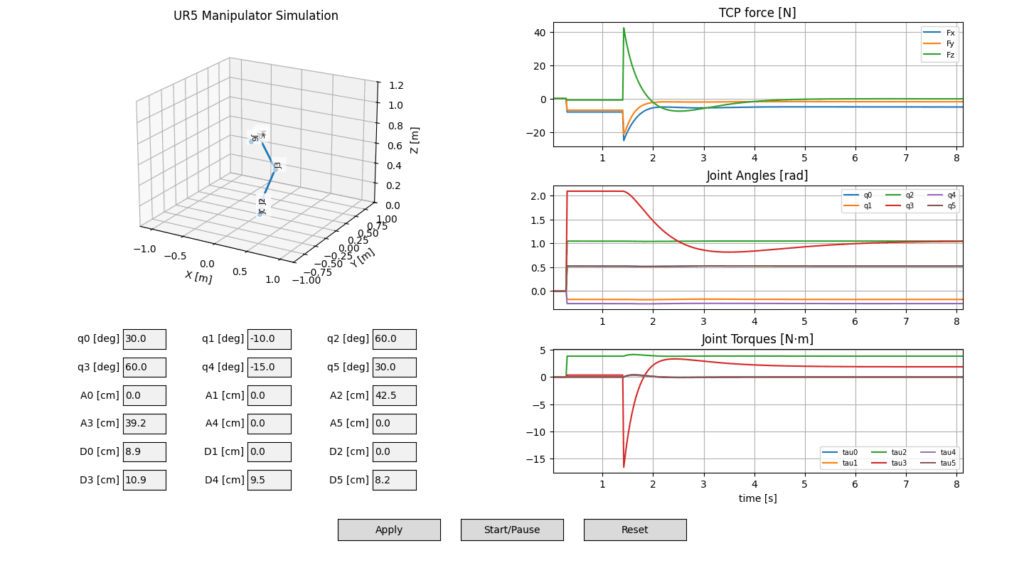
Figure 3. Force and Torque Damping Characteristics with the Conventional PID control.
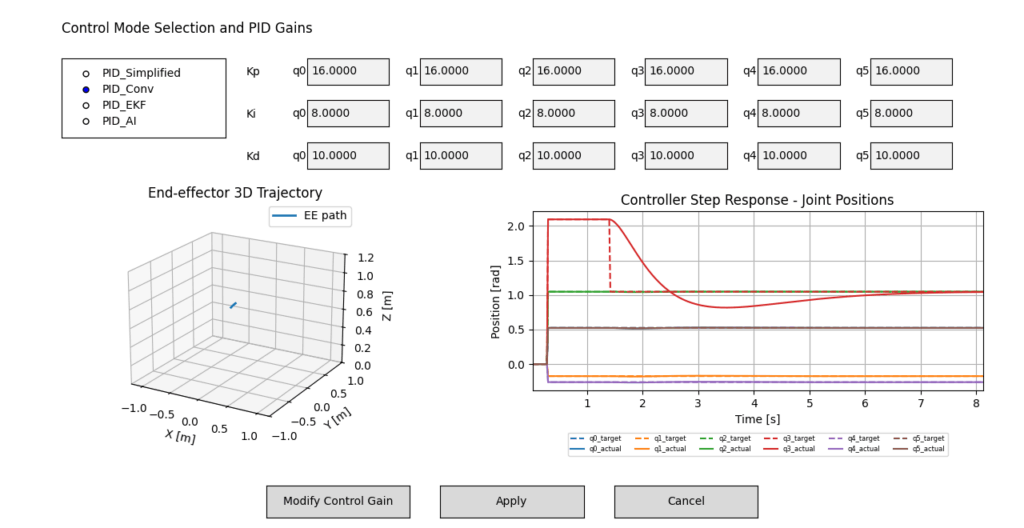
Figure 4. Control response of the Conventional PID control.
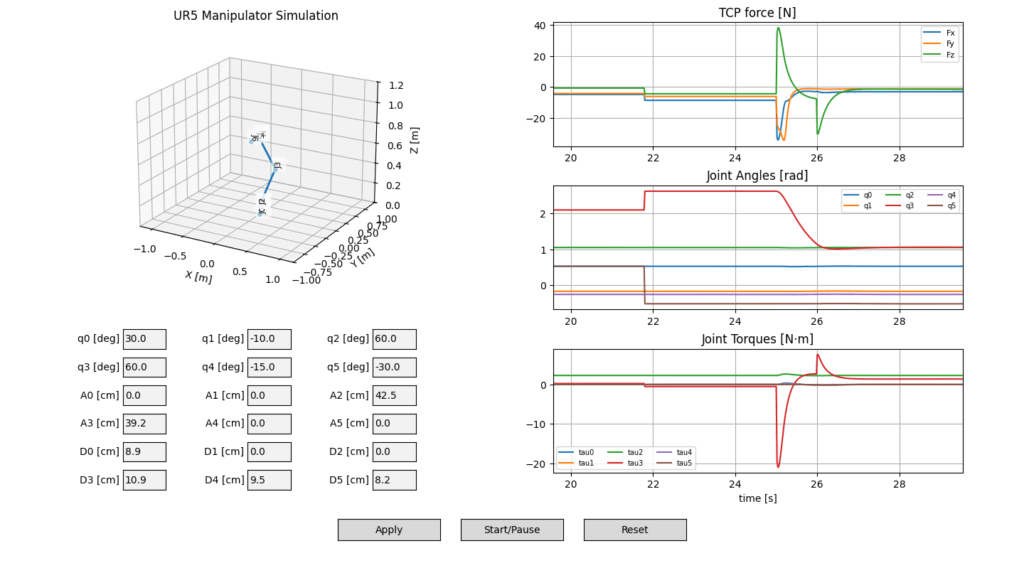
Figure 5. Force and Torque Damping characteristics with the time-delayed Extended Kalman Filter-based trajectory tracking control.
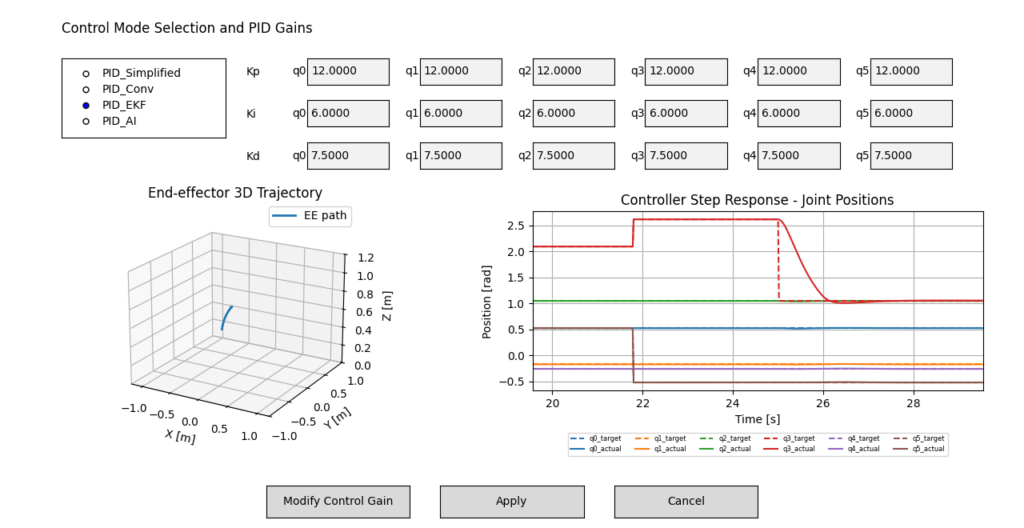
Figure 6. Control response of the time-delayed Extended Kalman Filter-based trajectory tracking control.